
Communication and sharing promote growth
Joining Hands for Development!

When your device has multiple core hot spots that are independent of each other, have varying power consumption, or require isolated cooling, traditional single-channel cold plates become inadequate. Multi-loop copper tube embedded cold plates are the key to overcoming this challenge.
1-Why Choose Multi-Loop? Three Scenarios That Address Key Pain Points
a.Isolate Thermal Interference to Ensure Core Unit Performance
When components such as IGBTs and diodes, or CPUs and GPUs, are densely arranged, a single flow channel can cause thermal "crosstalk," forcing low-temperature components to operate in high-temperature environments. The multi-loop design acts like a "dedicated air conditioner" for each component, completely eliminating thermal interference and ensuring each unit operates within its optimal temperature range, thereby enhancing overall system performance and stability.
b. Achieve System Redundancy for High-Reliability Architecture
In fields with extremely high reliability requirements, such as servers and communication base stations, the failure of a single cooling loop can lead to system downtime. The multi-loop design enables the construction of an "N+1" redundant cooling system. If one loop fails unexpectedly, the remaining loops can still provide basic cooling capacity, buying valuable time for system maintenance. This serves as the cornerstone of high-availability design.
c. Address Irregular Layouts and Differentiated Cooling Needs
For irregularly arranged heat sources, a single flow channel struggles to achieve uniform cooling. The multi-loop solution supports "tailored designs," allowing you to customize the path of each copper tube flexibly based on the actual shape and layout of the heat sources. This ensures optimal flow paths precisely covering every hot spot. Additionally, high-power consumption components can be assigned high-flow loops, while low-power consumption components can be assigned low-flow loops, achieving the optimal allocation of cooling resources.
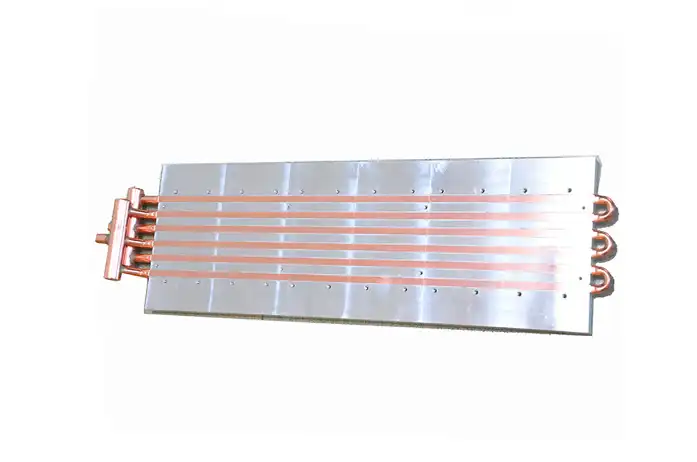
Figure 1: Multi-loop embedded copper tube cold plate
2-The Core of Design and Manufacturing: How to Balance Performance and Reliability in a Compact Space?
In multi-loop designs, the spacing between flow channels is critical to success.
a. Thermal Bottom Line: Preventing "Thermal Short Circuits"
If the spacing between adjacent flow channels is too narrow, even with independent channels, heat can rapidly conduct through the aluminum substrate in between, significantly compromising the isolation effect. Through simulation and testing, we have established a fundamental spacing principle of ≥1.5 times the tube diameter to ensure thermal independence.
b. Structural Red Line: Upholding the "Pressure-Bearing Lifeline"
The aluminum substrate between flow channels is a weak point for withstanding internal pressure. Excessively narrow spacing can lead to insufficient rib strength, posing a risk of tearing under pressure impact. Through mechanical stress simulation, we ensure that the stress between flow channels remains well below the material's yield limit under all operating conditions, fundamentally eliminating the risk of "plate rupture."
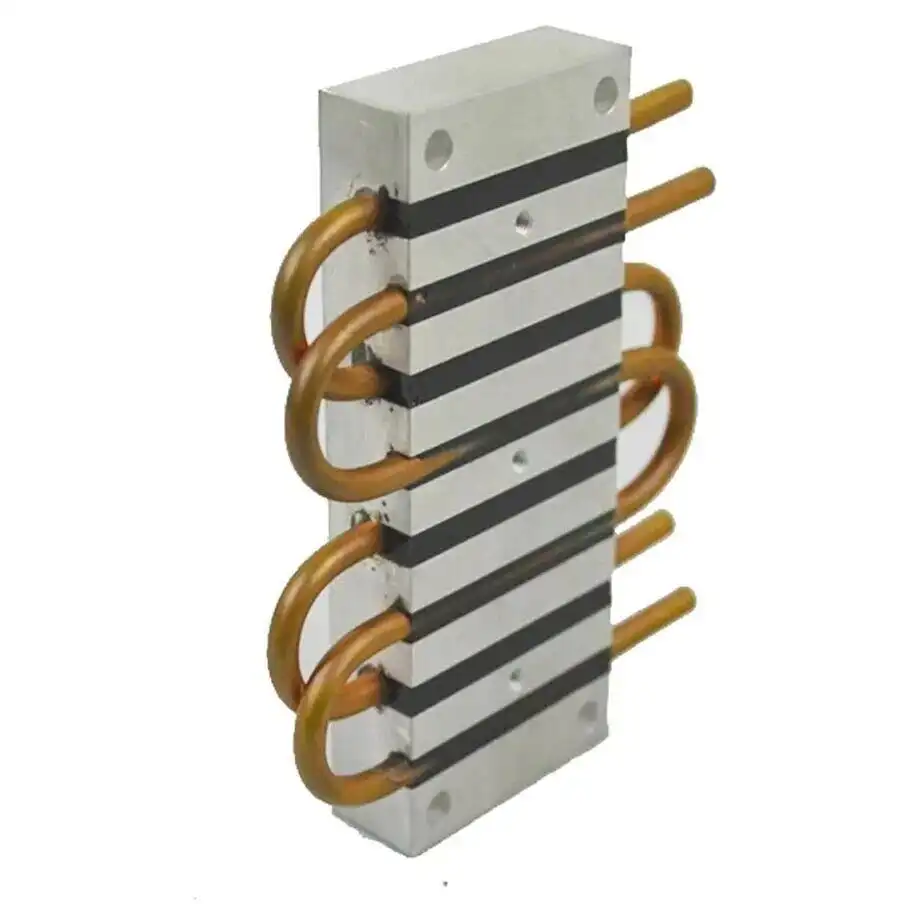

Figure 2: Embedded copper tube cold plate
c. Process Limits: Ensuring "Precision Manufacturing"
Narrow spacing poses a significant challenge for milling cutters. Based on extensive manufacturing experience, we correlate spacing with cutter diameter to ensure efficient machining while achieving smooth and flat channel walls. This lays the foundation for the subsequent tight nesting of copper tubes and low thermal resistance bonding.
3- Key Engineering Implementation Considerations
A successful multi-loop design requires attention to the following key aspects:
a. Collaborative Design
It is recommended to integrate thermal and mechanical design from the conceptual stage, taking into account flow channel layout, structural strength, and process capabilities to avoid subsequent design changes.
b. Process Control
• Utilize high-precision CNC milling for channels to ensure slot width tolerance and surface quality.
• Employ mandrel bending technology for copper tubes to maintain post-bending通畅性 and uniform wall thickness.
• Implement reliable nesting and fixation processes to prevent copper tube displacement under vibration conditions.
c. Verification Testing
A comprehensive testing system includes:
• 100% air tightness testing
• Flow rate–pressure drop characteristic testing
• Thermal resistance performance verification
• Burst pressure testing
In summary, multi-loop copper tube embedded cold plates are a powerful solution for addressing complex multi-heat source cooling challenges. The key to success lies in a deep understanding of their design logic and finding the optimal balance between performance and reliability.
We will regularly update you on technologies and information related to thermal design and lightweighting, sharing them for your reference. Thank you for your attention to Walmate.